Gamma, the Euler's constant
Gamma, the Euler's constant is defined
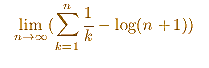
It also can be defined, equivalently, as
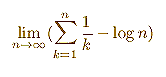
We use the first definition.
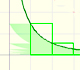
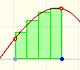
We can see that this series is bounded by 1 and is increasing. Each partial sum is obtained adding a "triangle" above the equilateral hyperbola. From the Bolzana-Weiestrass Theorem we can say that the series is convergent.
The symbol gamma was first used by Mascheroni.
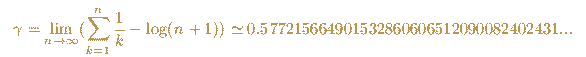
Gamma is an important constant in mathematics. It is suspected that it is an irrational number.
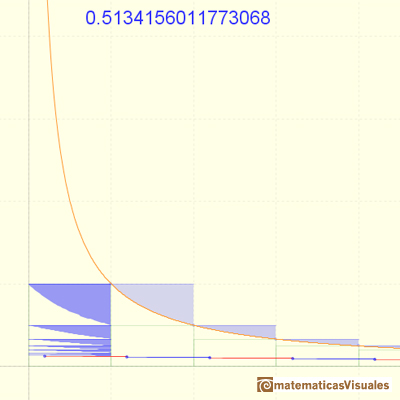
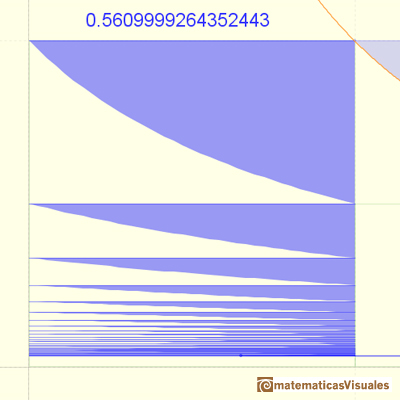
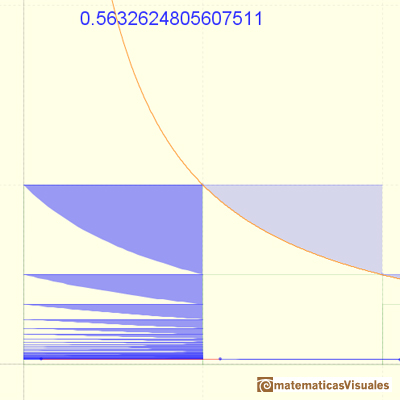
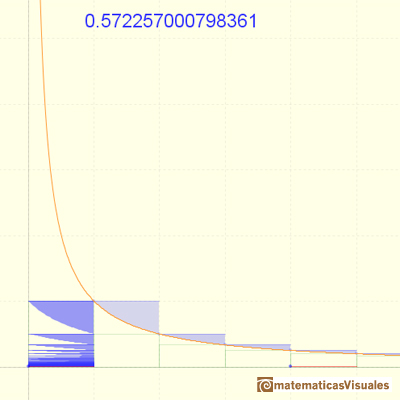
The convergence of the series is very slow.
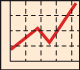
In the video we can see an animation that is approaching the value of Gamma.
The partial sums are limited by 1. The series is growing. The series is convergent and we can see that its value would be slightly larger than 0.5.
REFERENCES
William Dunham - Euler, The Master of Us All.
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS
MORE LINKS
The integral concept is associate to the concept of area. We began considering the area limited by the graph of a function and the x-axis between two vertical lines.
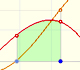
If we consider the lower limit of integration a as fixed and if we can calculate the integral for different values of the upper limit of integration b then we can define a new function: an indefinite integral of f.
We can see some basic concepts about integration applied to a general polynomial function. Integral functions of polynomial functions are polynomial functions with one degree more than the original function.
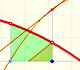
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus tell us that every continuous function has an antiderivative and shows how to construct one using the integral.
The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus is a powerful tool for evaluating definite integral (if we know an antiderivative of the function).
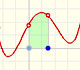
The Complex Cosine Function extends the Real Cosine Function to the complex plane. It is a periodic function that shares several properties with his real ancestor.
Inversion is a plane transformation that transform straight lines and circles in straight lines and circles.

The usual definition of a function is restrictive. We may broaden the definition of a function to allow f(z) to have many differente values for a single value of z. In this case f is called a many-valued function or a multifunction.
Multifunctions can have more than one branch point. In this page we can see a two-valued multifunction with two branch points.